Have you ever wondered why some electrical devices require a transformer to operate? Transformers are crucial components that either step up or step down the voltage to match the needs of your equipment. Whether you’re setting up a new appliance or installing outdoor lighting, understanding the difference between step-up and step-down transformers can help ensure you get the right one for the job.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the basics, so you can choose wisely next time you’re shopping for a transformer. A step-up transformer increases voltage, which is useful when powering devices that require higher voltage to operate properly. On the other hand, a step-down transformer reduces the voltage to a lower level, allowing you to power low-voltage equipment from a high-voltage power source.
Stay with us to learn how these essential devices work and find out which type of transformer is right for your next project. By the end, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a transformer expert and making the best choice for your needs.
What Is a Step-Up Transformer?
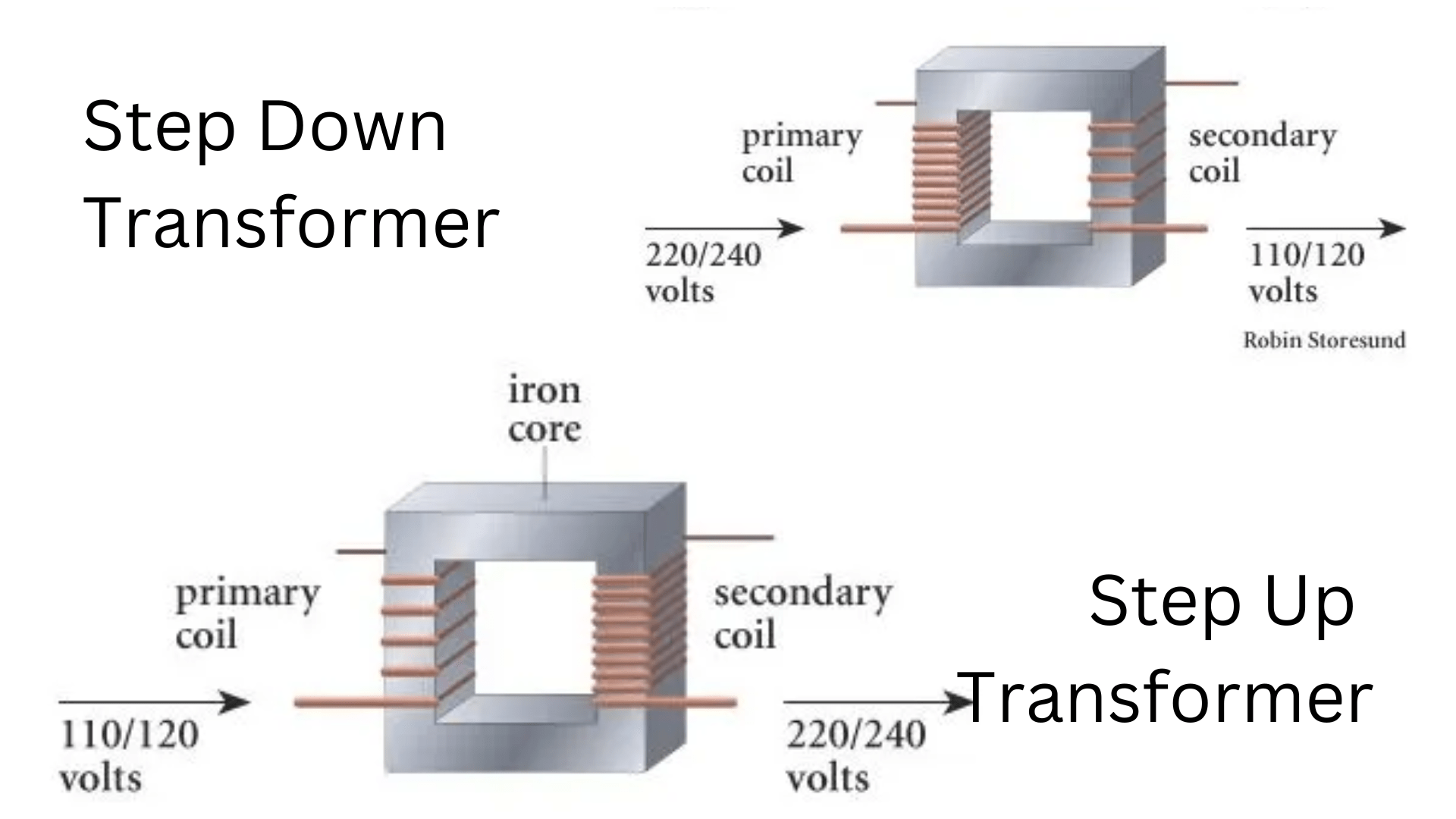
A step-up transformer is a device used in alternating current (AC) electrical systems to increase the voltage of a power supply. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, consisting of primary and secondary coils wound around a common core. When an AC current flows through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field, which induces a voltage in the secondary coil. This process results in the voltage being “stepped up” to a higher level compared to the input voltage.
Why would you need a step-up transformer? Several reasons:
- To reduce power loss over long distances. By increasing the voltage, less current is required to transmit the same amount of power. This means less energy is lost as heat during transmission.
- To be compatible with equipment that requires higher voltage to operate. Things like industrial equipment, electric furnaces, etc., may need 200V, 480V or higher to run properly. A step-up transformer takes the voltage to the required level.
- For more efficient power distribution. It’s easier to transmit power at high voltages and then step it down for end use. So utility companies will use step-up transformers to raise the voltage for transmission via power lines, then step it back down for homes and businesses.
The key is that a step-up transformer always boosts the voltage to a higher level. It never reduces voltage – for that, you need a step-down transformer. If you need to power equipment that calls for a lower voltage than the supply, a step-down transformer can take a higher input voltage and reduce it to the needed output level.
Together, step-up and step-down transformers allow us to efficiently generate, transmit and distribute electric power at the proper voltage levels for whatever the application may be. They form an indispensable part of our electrical infrastructure!
What Is a Step-Down Transformer?
A step-down transformer converts high voltage power into lower voltage power that’s suitable for use in homes and businesses. These transformers allow us to use the high-voltage electricity that’s distributed from power stations and make it safe for powering appliances, lights, and electronics.
Step-down transformers work by taking the input of high voltage power, like the 11,000 volts you’ll find on utility poles, and converting it into lower output voltages, such as the 220–240 volts used for large appliances or the 120 volts used for most household electronics. The transformer does this by using two coils of wire, a primary coil and a secondary coil. The primary coil takes in the high-voltage input and creates a magnetic field, which then induces a lower voltage in the secondary coil.
The most common types of step-down transformers are:
- Pole-mounted transformers: Those big cylinders you see on top of utility poles. They convert high voltage to the 240/120 volts that are distributed to homes.
- Pad-mounted transformers: For underground power distribution. They are located in those green metal boxes you see in neighbourhoods and convert high voltage to 240/120 volts.
- Substation transformers: Very large transformers located in electrical substations that convert extremely high transmission level voltages like 115,000 volts to lower primary distribution voltages of 11,000 volts or less.
So next time your lights come on as soon as you flip the switch, you can thank a step-down transformer for making that electricity safe and usable in your home. They are a crucial but often underappreciated part of power distribution systems all over the world.
The Key Differences Between Step-Up and Step-Down Transformers
The key differences between step-up and step-down transformers come down to their purpose and design. Each one plays an important role in the transmission of electrical power.
Step-Up Transformers
Step-up transformers are designed to increase voltage. They take power from a source with a lower voltage and convert it to a higher voltage for long-distance power transmission. The higher voltage allows for lower current, which means less energy is lost as heat during transmission. The low-voltage winding is the primary coil of a step-up transformer, and the high-voltage winding is the secondary winding.
Power companies use step-up transformers at the beginning of transmission lines near power plants to boost the voltage to hundreds of thousands of volts for transmission across long distances. Then step-down transformers lower the voltage again for distribution to homes and businesses.
Step-Down Transformers
Step-down transformers decrease the voltage to lower, safer levels that can be used in homes and businesses. They take the higher voltage from transmission lines and reduce it to standard utilisation voltages like 120V or 240V.
Step-down transformers are located throughout the power distribution network, including near your home or business. They ensure the final voltage delivered is suitable for powering your lights, electronics, and appliances.
The key distinction is that step-up transformers increase voltage, while step-down transformers decrease voltage. Both are critical components that make transmitting and distributing electrical power possible. Together, they help deliver safe, usable power for homes and businesses everywhere.
Choosing Between a Step-Up or Step-Down Transformer
Choosing between a step-up or step-down transformer depends on your specific needs. If you need to increase the voltage, you’ll want a step-up transformer. If you need to decrease the voltage, choose a step-down transformer.
A step-up transformer is used when you have a power source with a lower voltage that needs to be increased to a higher voltage. For example, if you have a 120V power source but need 240V to power certain equipment, you’d use a step-up transformer to boost the voltage. Step-up transformers are commonly used when connecting low-voltage circuits to high-voltage transmission lines.
On the other hand, a step-down transformer reduces the voltage from a higher level to a lower one. This is useful when powering low-voltage devices like electronics. For instance, the utility company provides power at a higher voltage, which is then stepped down to the standard 120V for residential use. Step-down transformers are also used for applications where a lower voltage is safer, such as powering landscape lighting, toys or other consumer goods.
Also Read: Understanding The Basics of Distribution Transformers
Other Considerations
Here are a few other things to keep in mind when choosing a transformer:
• Power rating – Make sure the transformer can handle the amount of power you need. Higher power transformers tend to be larger and more expensive.
• Number of windings – Transformers typically have two windings, a primary winding and a secondary winding. But some have multiple secondaries to provide different voltage outputs.
• Efficiency – Look for “energy efficient” or low-loss transformers that minimise wasted energy released as heat. More efficient transformers tend to cost a bit more upfront but can save money in the long run.
• Indoor vs outdoor – Choose an outdoor, weather-resistant transformer for outdoor applications. Indoor transformers should only be used inside.
• Cost – In general, step-up transformers tend to cost slightly more than step-down transformers. Prices vary depending on the power rating and quality.
In the end, determining whether you need a step-up or step-down transformer comes down to your specific application and voltage needs. Evaluate your requirements carefully so you choose a transformer that’s properly suited for the job.
Conclusion
So now you have a better understanding of the key differences between step-up and step-down transformers. While they may seem similar at first glance, they each serve a very different purpose in electrical systems by either increasing or decreasing voltage. The next time you see one of those familiar cylindrical transformers up on an electrical pole or in a substation, you’ll know exactly what it’s doing to keep power flowing to your home or business. Though transformers themselves may not seem exciting, they play such an important role in making modern life possible. Pretty cool that such a fundamental bit of technology still works so reliably after all these years.
So, contact us immediately to learn more about transformers and how we can meet your needs!